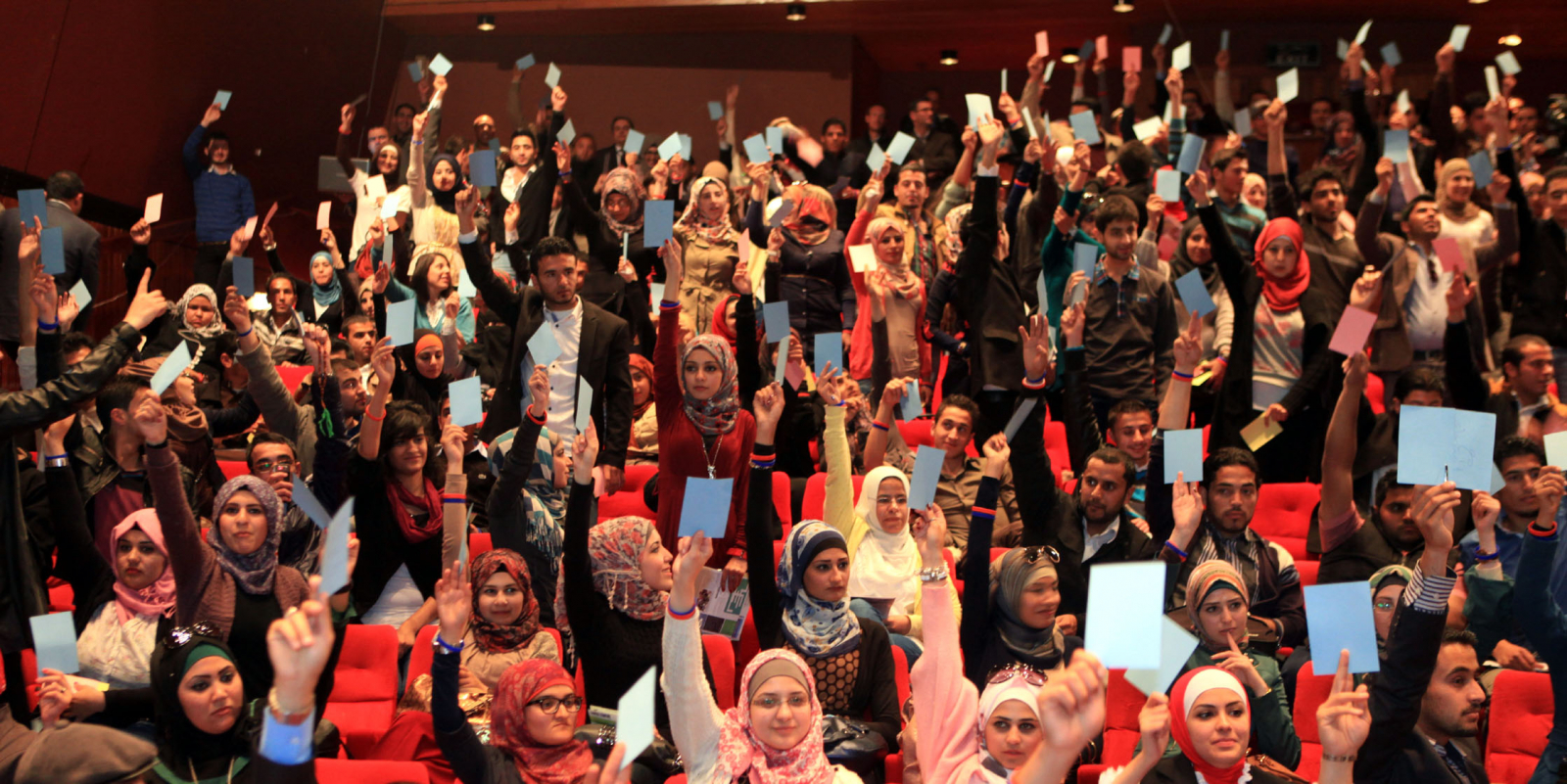
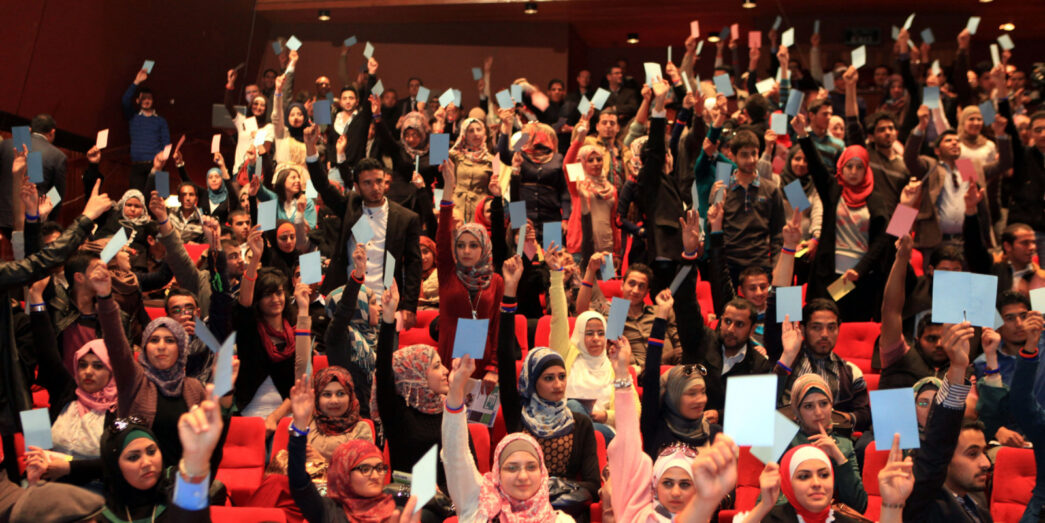
Jordan has long been a beacon of stability in the Middle East, but it has not been immune to social movements driven by demands for reform and accountability. Over the years, young Jordanians have emerged as key players in shaping the nation’s social and political landscape. From grassroots activism to digital campaigns, these movements reflect a push for change in governance, economic policies, and societal norms. Here’s a closer look at how social movements in Jordan are fostering youth engagement and driving political reform.
The Role of Youth in Social Movements
- Demographic Advantage
- Over 60% of Jordan’s population is under 30, making youth a significant force for change.
- Young people are at the forefront of calls for improved governance, job opportunities, and political inclusivity.
- Digital Activism
- Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have become powerful tools for organizing protests, spreading awareness, and amplifying voices.
- Examples: Campaigns such as “Hirak Shababi” (Youth Movement) focus on issues like corruption and economic inequality.
- Education and Awareness
- Increased access to education has empowered Jordanian youth with knowledge of their rights and the skills to articulate their demands effectively.
Key Social Movements in Jordan
- The Arab Spring Influence (2011)
- Inspired by uprisings in neighboring countries, Jordanians took to the streets to demand political and economic reforms.
- Outcomes: Amendments to the constitution and promises of greater parliamentary representation.
- Anti-Corruption Protests
- Movements targeting corruption in public offices have gained traction, driven by demands for transparency and accountability.
- Example: Protests against tax hikes in 2018 highlighted frustrations with economic mismanagement.
- Economic Justice Movements
- Youth-driven protests focus on unemployment, poverty, and wage disparities, advocating for fairer economic policies and job creation.
- Example: The “Bread Subsidy Protests” in 2018 demonstrated the public’s resistance to austerity measures.
- Women’s Rights Campaigns
- Women in Jordan have been actively fighting for gender equality, tackling issues like unequal inheritance laws and domestic violence.
- Example: The abolition of Article 308 in 2017, which allowed rapists to avoid punishment by marrying their victims.
- Environmental Activism
- Movements addressing water scarcity, renewable energy, and waste management are gaining momentum.
- Example: Initiatives to protect Jordan’s forests and reduce pollution in urban areas.
Challenges Facing Social Movements
- Limited Political Representation
- While some reforms have been introduced, youth and women remain underrepresented in decision-making processes.
- Economic Constraints
- High unemployment rates and economic instability often overshadow long-term activism.
- Government Restrictions
- Protest laws and restrictions on public gatherings can stifle large-scale movements.
- Fragmentation
- Lack of unified leadership and coordination among movements can dilute their impact.
Government Response to Social Movements
- Reforms and Dialogues
- The government has introduced political reforms, such as changes to electoral laws and the decentralization of power, in response to public demands.
- Youth Engagement Programs
- Initiatives like the Crown Prince Foundation aim to empower young Jordanians through leadership programs and skill development.
- Economic Initiatives
- Programs to support entrepreneurship and job creation, such as grants and loans for startups, target youth unemployment.
The Role of Civil Society and International Organizations
- Support for Activism
- NGOs and international organizations provide resources and platforms for training, advocacy, and community engagement.
- Example: USAID-funded programs promoting civic participation and governance reforms.
- Media and Awareness Campaigns
- Civil society groups use traditional and digital media to amplify the voices of marginalized communities and advocate for policy changes.
Future Prospects for Social Movements in Jordan
- Increased Digital Mobilization
- As internet access expands, digital activism will continue to play a critical role in organizing and spreading awareness.
- Youth Leadership Development
- Training programs and mentorship initiatives will cultivate the next generation of leaders.
- Global Solidarity
- Collaboration with international movements and organizations can bring new strategies and resources to Jordanian activism.
- Sustainable Reforms
- Long-term success will depend on the government’s ability to implement meaningful reforms and address the root causes of social discontent.
Social movements in Jordan, led by its vibrant and determined youth, are reshaping the country’s political and social fabric. While challenges remain, these movements reflect a deep commitment to creating a more inclusive, transparent, and equitable society. By embracing youth engagement and addressing the demands of its people, Jordan has the potential to set an example for peaceful reform in the Middle East.
Topics: Arab Spring Digital Activism Economic Justice Gender Equality Jordan Government Reforms Jordanian Protests Middle East Politics Political Reform Social Movements In Jordan Youth Activism