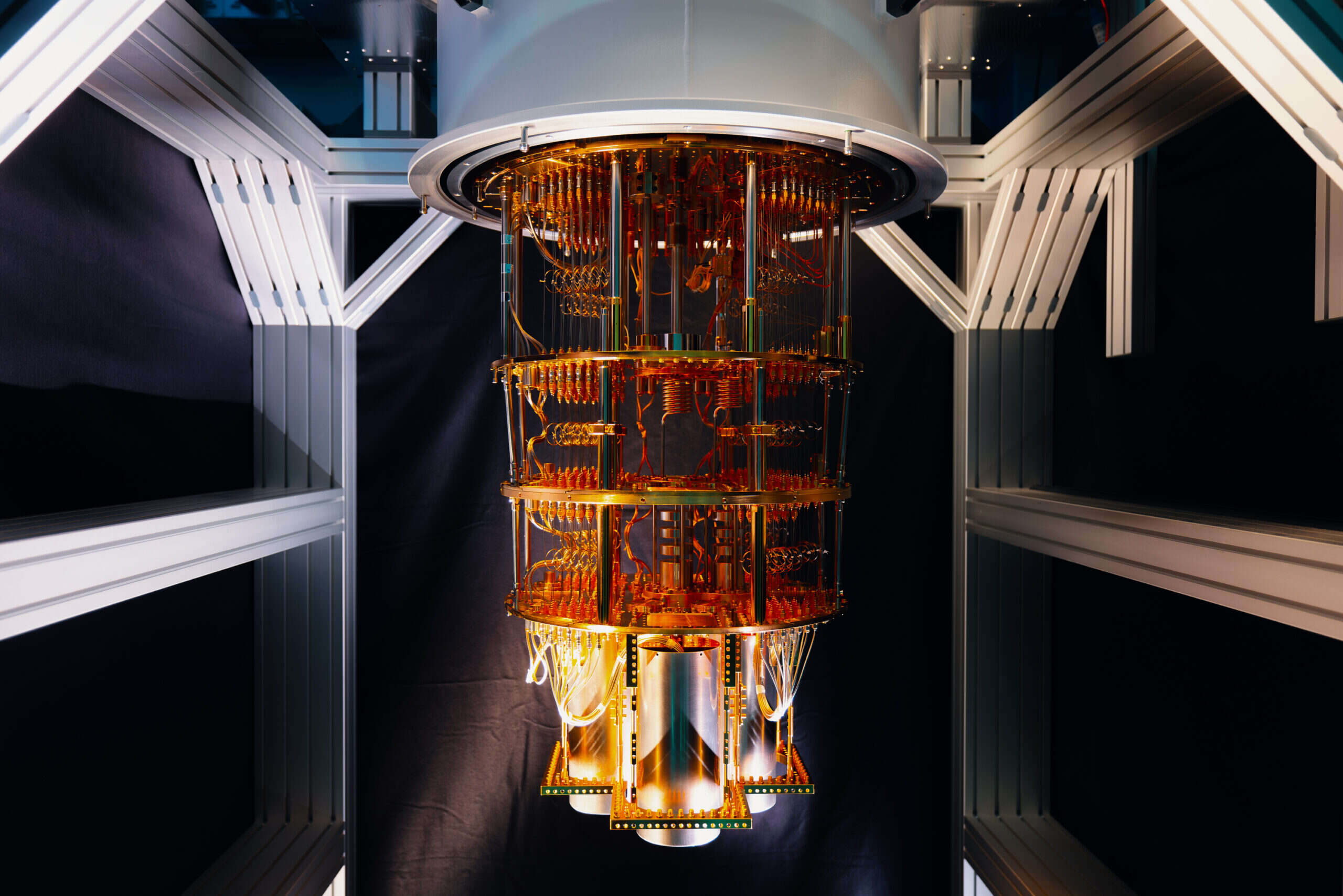
Quantum computing is no longer a concept confined to theoretical physics—it’s becoming a reality with the potential to revolutionize industries and solve problems far beyond the capabilities of classical computers. As we stand on the brink of this technological breakthrough, understanding quantum computing and its implications is more important than ever.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics, the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of particles at the smallest scales. Unlike classical computers, which use bits (0s and 1s) to process information, quantum computers use qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously thanks to superposition.
Key principles include:
- Superposition: Qubits can represent both 0 and 1 at the same time, exponentially increasing computational power.
- Entanglement: Qubits can be interconnected, so the state of one can depend on the state of another, enabling ultra-fast information sharing.
- Quantum Tunneling: Allows quantum systems to bypass certain computational barriers, solving problems faster.
How Does Quantum Computing Work?
- Initialization: Qubits are prepared in a specific quantum state.
- Processing: Algorithms manipulate these states using quantum gates, which control the behavior of qubits.
- Measurement: The quantum state collapses into a classical state (0 or 1) to provide the final result.
Applications of Quantum Computing
- Drug Discovery and Healthcare
- Quantum computing can simulate molecular interactions at an atomic level, accelerating drug development.
- It could revolutionize personalized medicine by analyzing complex genetic data.
- Cryptography
- Quantum computers have the potential to break traditional encryption methods, prompting the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic techniques.
- They also offer secure communication channels through quantum key distribution.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Quantum computing enhances machine learning by optimizing complex algorithms, improving data training and pattern recognition.
- Optimization Problems
- From supply chain logistics to financial portfolio management, quantum computers can solve optimization problems faster than classical systems.
- Climate Modeling
- Quantum simulations provide more accurate climate models, enabling better predictions and solutions to combat climate change.
Challenges of Quantum Computing
- Fragility of Qubits:
- Qubits are highly sensitive to environmental disturbances, leading to errors in computation.
- Scalability:
- Building large-scale, stable quantum computers remains a challenge.
- Cost:
- Quantum computers require specialized environments, such as extremely low temperatures, making them expensive to develop and maintain.
- Talent Gap:
- Quantum computing demands expertise in quantum physics, mathematics, and computer science, creating a shortage of skilled professionals.
Quantum Computing vs. Classical Computing
| Feature | Quantum Computing | Classical Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Representation | Qubits (0, 1, or both simultaneously) | Bits (0 or 1) |
| Processing Speed | Exponentially faster for certain tasks | Limited by binary operations |
| Applications | Complex simulations, optimization | Everyday tasks, general use |
The Future of Quantum Computing
The next decade will likely see quantum computing transition from experimental to practical applications. Key developments include:
- Commercial Quantum Services: Companies like IBM, Google, and Microsoft are offering cloud-based quantum computing platforms.
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: Governments and businesses are investing in secure quantum encryption.
- Collaboration Across Industries: Quantum computing will drive innovation in fields like artificial intelligence, finance, and energy.
Quantum computing represents a leap into the future, offering unprecedented computational power and the ability to tackle some of humanity’s most complex problems. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are immense. By understanding and investing in quantum technology, we can unlock solutions that were once considered impossible, transforming industries and improving lives worldwide.
The quantum revolution is here—are you ready?
Topics: Emerging Technology Future of Computing Quantum Applications Quantum Computing Quantum Mechanics Qubits