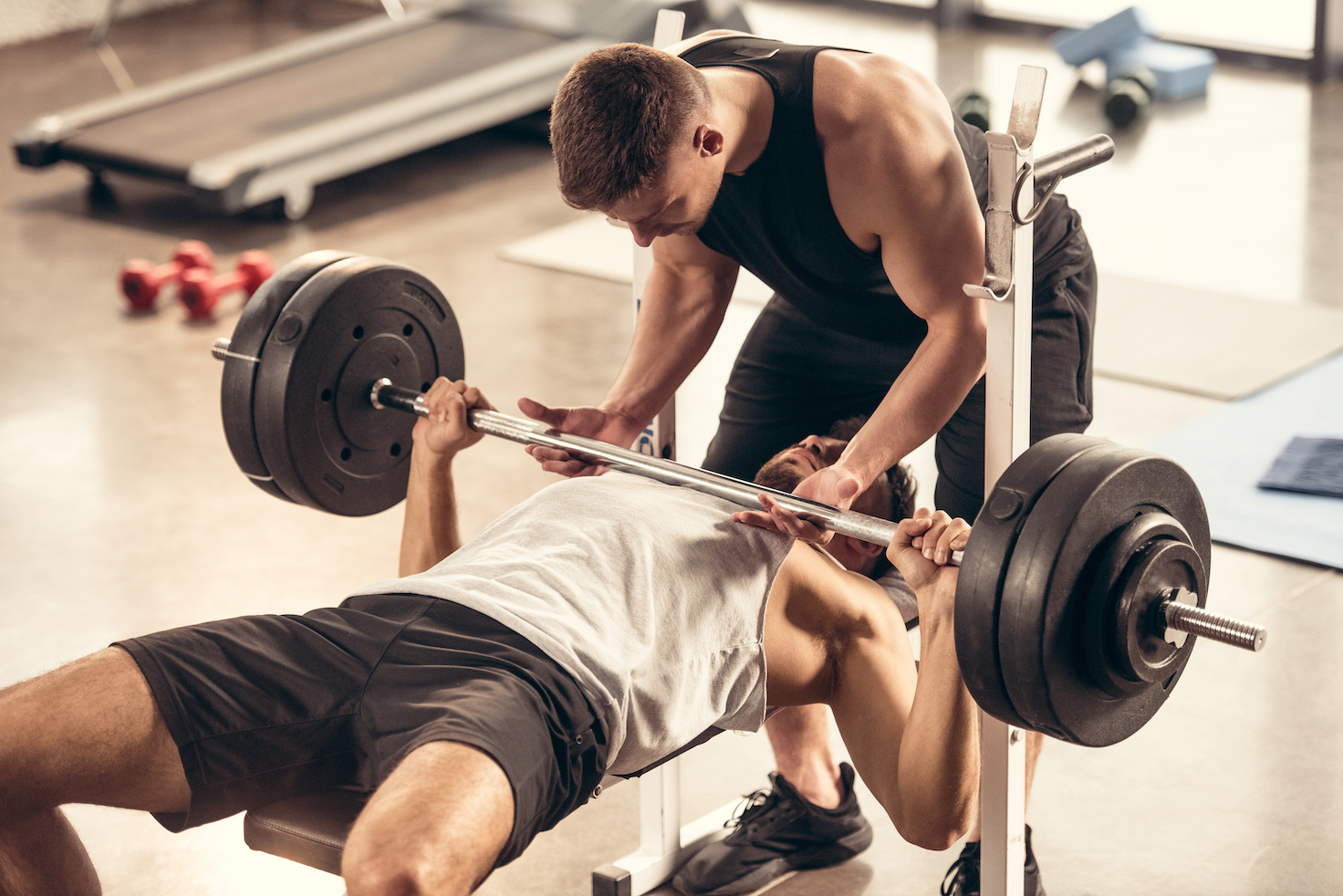
Muscular strength is a vital component of physical fitness, referring to the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to exert force during an activity. Building muscular strength not only enhances your physical performance but also supports overall health, including bone density, joint stability, and metabolic function. Whether you’re lifting weights, carrying groceries, or playing sports, strong muscles are essential for daily activities and long-term well-being.
What is Muscular Strength?
Muscular strength is the maximum amount of force a muscle can generate in a single effort. It is typically measured by exercises like lifting weights, performing push-ups, or completing resistance-based activities.
Key factors that influence muscular strength:
- Muscle Size: Larger muscles can produce more force.
- Neural Adaptations: Improved coordination between the nervous system and muscles enhances strength.
- Type of Training: Consistent resistance training builds strength over time.
Benefits of Muscular Strength
- Enhanced Physical Performance:
- Improves performance in sports, physical labor, and everyday activities.
- Increased Metabolic Rate:
- Muscles burn more calories than fat, even at rest, aiding in weight management.
- Improved Joint Health:
- Strengthens muscles around joints, reducing the risk of injury and conditions like arthritis.
- Better Posture and Stability:
- Supports the spine and improves alignment, reducing back pain and enhancing balance.
- Boosted Mental Health:
- Strength training releases endorphins, reducing stress and improving mood.
- Enhanced Bone Density:
- Weight-bearing exercises promote stronger bones, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Exercises to Build Muscular Strength
- Bodyweight Exercises:
- Push-ups: Strengthen chest, shoulders, and triceps.
- Planks: Build core stability and endurance.
- Squats: Target lower body muscles, including quads, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Weightlifting:
- Bench Press: Builds chest and upper body strength.
- Deadlift: Targets the back, glutes, and hamstrings.
- Bicep Curls: Isolate and strengthen the biceps.
- Resistance Band Exercises:
- Rows: Strengthen the back and shoulders.
- Lateral Band Walks: Engage glutes and hips.
- Functional Strength Training:
- Kettlebell Swings: Enhance explosive power and endurance.
- Farmer’s Carry: Improve grip strength and stability.
- Compound Movements:
- Pull-Ups: Work multiple muscle groups, including arms and back.
- Lunges with Weights: Strengthen the legs while improving balance.
How to Measure Muscular Strength
- One-Rep Max (1RM):
- The maximum weight you can lift for one repetition in an exercise.
- Example: Bench press or squat 1RM.
- Grip Strength Test:
- Measures hand and forearm strength using a dynamometer.
- Functional Assessments:
- Tests like push-ups or sit-to-stand evaluate strength in practical activities.
Tips for Building Muscular Strength
- Follow the Progressive Overload Principle:
- Gradually increase the weight, reps, or intensity of your workouts to challenge your muscles.
- Incorporate Rest and Recovery:
- Allow muscles time to repair and grow stronger by taking rest days or alternating muscle groups.
- Focus on Form:
- Use proper technique to prevent injury and ensure maximum effectiveness.
- Eat for Strength:
- Consume a protein-rich diet to support muscle repair and growth.
- Include complex carbohydrates for sustained energy.
- Stay Consistent:
- Aim for 2–4 strength-training sessions per week for optimal results.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overtraining:
- Not allowing enough recovery time can lead to muscle fatigue and injuries.
- Neglecting Smaller Muscle Groups:
- Focus on a balanced routine that targets all major muscle groups, including core and stabilizing muscles.
- Improper Technique:
- Lifting with poor form increases the risk of injury and reduces workout effectiveness.
- Skipping Warm-Ups:
- Always warm up to prepare muscles and prevent strains.
Muscular Strength vs. Muscular Endurance
- Muscular Strength:
- Focuses on maximum force production in short bursts (e.g., lifting heavy weights).
- Muscular Endurance:
- Involves sustaining repeated contractions over a longer period (e.g., performing multiple push-ups).
Both are important for overall fitness and can complement each other in a balanced workout routine.
Incorporating Strength Training into Daily Life
- Functional Movements:
- Carry heavy groceries, climb stairs, or garden to integrate strength-building activities into daily routines.
- At-Home Workouts:
- Use resistance bands, dumbbells, or bodyweight exercises to build strength without needing a gym.
- Join a Class:
- Group classes like CrossFit or circuit training can provide structure and motivation.
Muscular strength is a cornerstone of fitness that enhances your physical capabilities, supports overall health, and boosts confidence. Whether you’re lifting weights, practicing bodyweight exercises, or exploring functional training, focusing on building strength can lead to a healthier and more active lifestyle. Start small, stay consistent, and watch your strength grow—one rep at a time.
Are you ready to unlock your full potential and build a stronger, more resilient body?
Topics: Bodyweight Exercises Fitness Tips Muscle Growth Muscular Strength Physical Health Strength Training Weightlifting