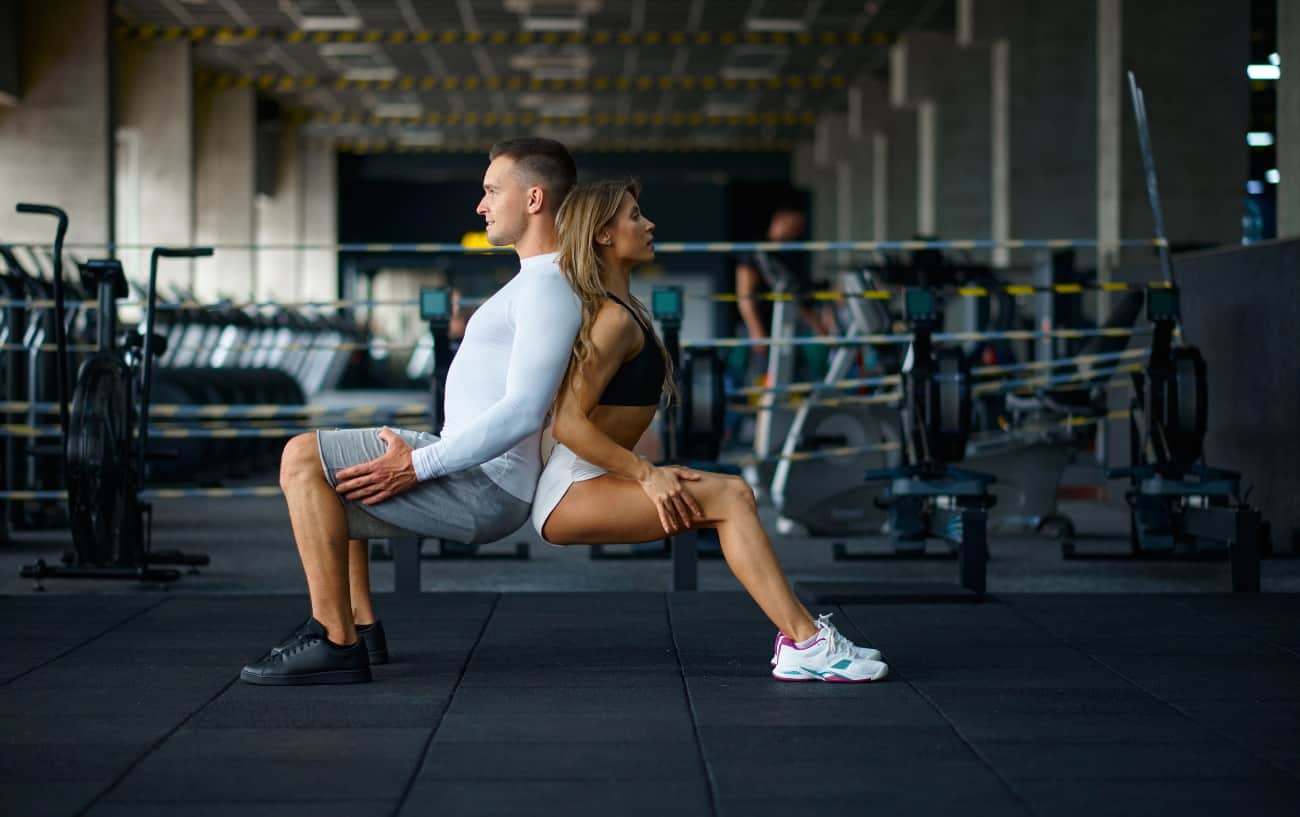
Muscular endurance is the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to perform repeated contractions or sustain force over an extended period. It’s a critical component of fitness, enabling you to carry out daily activities, excel in sports, and maintain good posture without experiencing premature fatigue. Whether you’re an athlete or someone looking to improve functional strength, building muscular endurance can enhance your performance and overall quality of life.
What is Muscular Endurance?
Muscular endurance measures how long your muscles can perform a task before becoming exhausted. It differs from muscular strength, which focuses on the maximum amount of force muscles can generate in a single effort.
Examples of muscular endurance activities:
- Holding a plank for as long as possible.
- Performing multiple push-ups or squats without rest.
- Running long distances where muscles sustain repetitive motion.
Benefits of Muscular Endurance
- Improved Physical Performance:
- Enhances stamina for activities like cycling, swimming, or hiking.
- Increased Daily Functionality:
- Makes tasks like carrying groceries, climbing stairs, or yard work easier.
- Better Posture and Stability:
- Strengthens core and stabilizing muscles to support proper alignment.
- Reduced Risk of Injury:
- Builds resilient muscles that can handle repetitive movements without strain.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance:
- Crucial for sports requiring sustained effort, such as soccer, rowing, or tennis.
- Boosted Metabolic Health:
- Repetitive muscle activation burns calories and improves overall endurance.
Examples of Muscular Endurance Exercises
- Bodyweight Exercises:
- Push-ups: Improve upper body endurance.
- Planks: Build core stability and endurance.
- Squats: Strengthen lower body muscles.
- Cardio with Resistance:
- Cycling: Targets leg muscles with sustained effort.
- Rowing: Engages multiple muscle groups in rhythmic motion.
- Swimming: Builds endurance in the arms, legs, and core.
- Circuit Training:
- Combines strength and cardio exercises in a sequence to boost muscular endurance.
- Example: Push-ups, burpees, and jump squats in a timed circuit.
- High-Rep Weight Training:
- Focuses on lighter weights with higher repetitions (12-20 reps).
- Example: Dumbbell curls or lunges with light weights.
- Functional Movements:
- Activities like carrying a heavy bag over a distance or climbing stairs repeatedly.
How to Build Muscular Endurance
- Progressive Overload:
- Gradually increase the number of repetitions, sets, or workout duration over time.
- Consistency:
- Incorporate endurance-focused exercises into your routine 2-3 times per week.
- Incorporate Intervals:
- Alternate between high-intensity bursts and lower-intensity recovery periods to improve stamina.
- Combine Strength and Cardio:
- Blend resistance exercises with aerobic activities to target multiple muscle groups.
- Rest and Recover:
- Allow muscles time to repair and grow by including rest days in your schedule.
Measuring Muscular Endurance
- Push-Up Test:
- Count how many push-ups you can perform without stopping.
- Plank Test:
- Measure how long you can hold a plank position with proper form.
- Sit-Up Test:
- Record the number of sit-ups completed in a minute.
- Time-Based Activities:
- Track how long you can sustain repetitive activities like cycling or rowing.
Muscular Endurance vs. Muscular Strength
| Aspect | Muscular Endurance | Muscular Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to sustain activity over time | Maximum force a muscle can exert in one effort |
| Exercise Type | High reps, low resistance | Low reps, high resistance |
| Example Activity | Cycling, planking, high-rep squats | Deadlifting, bench pressing |
| Primary Goal | Stamina and fatigue resistance | Power and maximum force |
Tips for Improving Muscular Endurance
- Set Clear Goals:
- Decide whether you want to focus on specific activities like running, swimming, or general stamina.
- Engage in Multi-Muscle Exercises:
- Focus on compound movements like squats and lunges that engage multiple muscle groups.
- Focus on Proper Form:
- Avoid injury by maintaining correct posture during exercises.
- Hydration and Nutrition:
- Fuel your body with a balanced diet rich in protein, complex carbs, and healthy fats.
- Incorporate Variety:
- Alternate between different exercises and formats to keep your routine engaging.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overtraining:
- Failing to rest can lead to muscle fatigue and increased risk of injury.
- Ignoring Other Fitness Components:
- While focusing on endurance, also include strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular exercises for overall fitness.
- Using Improper Technique:
- Poor form reduces effectiveness and increases the risk of strain.
- Skipping Warm-Up and Cool-Down:
- Always prepare your muscles before exercising and stretch after to prevent soreness.
Muscular Endurance in Daily Life
- Carrying Groceries: Repeatedly lifting and transporting bags requires sustained muscle effort.
- Walking Long Distances: Endurance in the legs and core makes long walks less tiring.
- Playing with Children: Activities like running, lifting, and playing sports with kids demand endurance.
Conclusion
Muscular endurance is a vital aspect of fitness that enhances your ability to perform activities efficiently and without fatigue. By incorporating endurance-focused exercises into your routine and maintaining consistency, you can improve your stamina, reduce the risk of injury, and enjoy a more active lifestyle. Whether you’re training for a marathon or simply looking to carry out daily tasks with ease, building muscular endurance is key to achieving your goals.
Are you ready to strengthen your endurance and unlock your full potential?
Topics: Fitness Tips Functional Training High-Rep Workouts Muscular Endurance Physical Health Stamina Strength Training