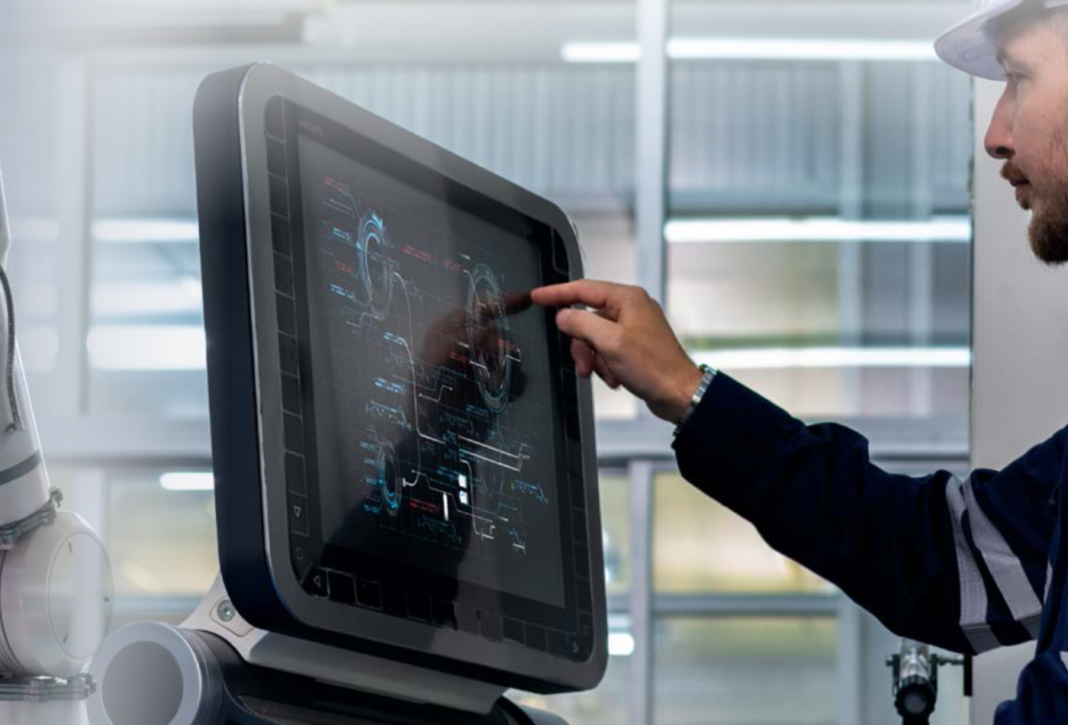
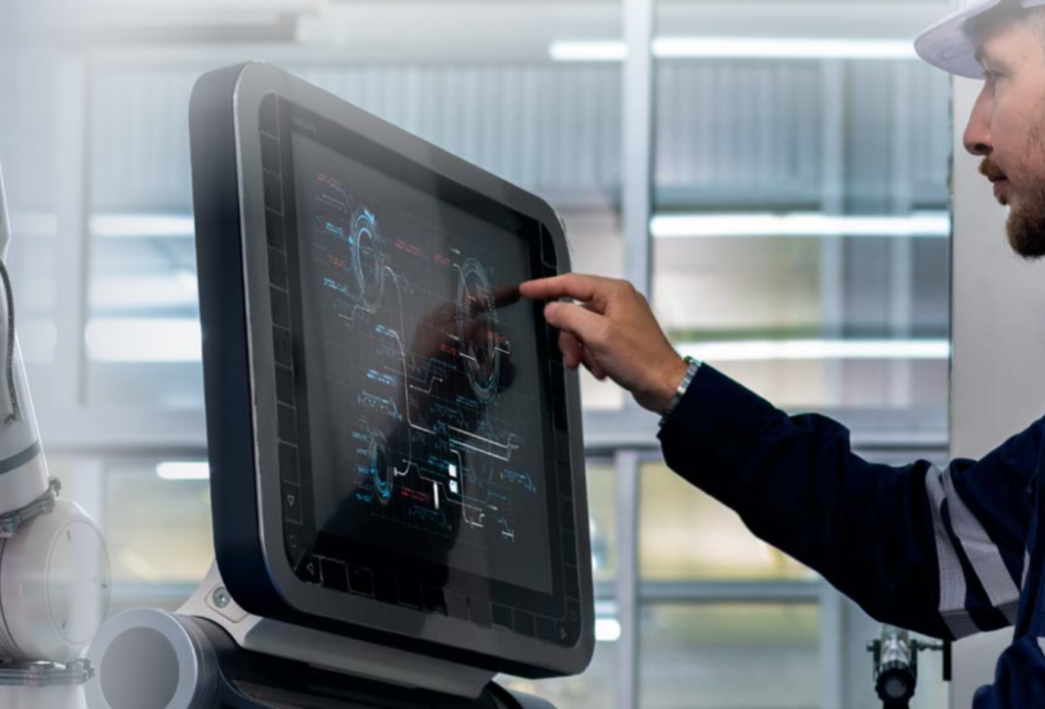
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) are revolutionizing how we interact with technology, enabling seamless communication between humans and machines. From touchscreens and voice commands to brain-computer interfaces, HMI technologies are reshaping industries and enhancing user experiences. Here’s an in-depth look at HMIs, their applications, and their future potential.
What is a Human-Machine Interface (HMI)?
HMI refers to the hardware and software systems that allow humans to interact with machines and devices. It translates human inputs—such as touch, voice, or gestures—into commands that a machine can understand and execute.
Key features of modern HMIs:
- Intuitiveness: Designed to be user-friendly and accessible.
- Real-Time Feedback: Provides immediate responses to user actions.
- Customization: Tailored interfaces for specific industries and applications.
Applications of Human-Machine Interfaces
1. Industrial Automation
- HMIs are widely used in manufacturing and industrial settings to monitor and control machinery.
- Example: Touchscreen panels on factory floors provide real-time data on equipment performance and enable remote adjustments.
2. Automotive Industry
- Advanced HMIs in vehicles enhance safety and convenience.
- Examples: Voice-activated navigation systems, heads-up displays (HUDs), and gesture-based controls for infotainment systems.
3. Healthcare
- HMIs play a critical role in medical devices, allowing healthcare professionals to monitor and control equipment.
- Example: Touchscreen interfaces on diagnostic tools and wearable devices that provide real-time patient data.
4. Consumer Electronics
- Smartphones, tablets, and smart home devices rely on HMIs for intuitive user experiences.
- Examples: Touchscreens, voice assistants (e.g., Alexa, Siri), and gesture-controlled smart TVs.
5. Gaming and Virtual Reality (VR)
- Immersive HMIs like VR headsets and motion-tracking controllers provide enhanced gaming experiences.
- Example: Controllers that simulate touch and motion for a more realistic experience.
6. Aerospace and Defense
- HMIs are used in flight control systems, navigation, and mission planning.
- Example: Heads-up displays in fighter jets that provide critical data without distracting pilots.
Emerging HMI Technologies
- Voice Recognition and Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Voice-activated HMIs are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling natural conversations with devices.
- Gesture-Based Interfaces
- Gesture recognition systems track hand movements to control devices without physical contact.
- Example: Smart TVs that respond to hand gestures for volume control and channel selection.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs)
- BCIs connect directly to the human brain, allowing users to control devices through thought.
- Potential applications include assisting individuals with disabilities and enhancing VR experiences.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
- AR and VR HMIs create immersive environments where users can interact with digital objects in real-time.
- Example: AR glasses that overlay digital information onto the physical world.
- Haptic Feedback Systems
- Haptic interfaces provide tactile sensations, simulating the feeling of touch to enhance user interaction.
- Example: VR gloves that mimic the sensation of holding objects.
Benefits of HMIs
- Enhanced User Experience:
- Intuitive and responsive interfaces improve usability and accessibility.
- Increased Efficiency:
- Streamlined workflows and real-time feedback boost productivity in industrial and professional settings.
- Safety:
- Hands-free and voice-activated systems reduce distractions and risks, especially in automotive and healthcare applications.
- Customization:
- HMIs can be tailored to specific user needs, ensuring optimal functionality and convenience.
Challenges in HMI Development
- Complexity of Design:
- Creating intuitive yet powerful interfaces requires balancing functionality with simplicity.
- Data Security:
- HMIs connected to sensitive systems are vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Cost:
- Advanced HMI technologies, such as BCIs and AR systems, remain expensive to develop and deploy.
- User Adaptation:
- Training may be required for users to fully leverage complex HMI systems.
The Future of Human-Machine Interfaces
The next generation of HMIs will further blur the line between humans and machines. Emerging trends include:
- AI-Driven Interfaces: AI will enable HMIs to predict user needs and adapt dynamically.
- BCI Integration: Brain-computer interfaces will become more accessible, enabling thought-controlled devices.
- Multisensory Experiences: HMIs will combine visual, auditory, and tactile feedback for more immersive interactions.
- Universal Interfaces: Standardized HMI systems that work across multiple devices and platforms.
Human-Machine Interfaces are at the core of our interaction with technology, bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds. As HMI technologies continue to evolve, they promise to make our lives safer, more efficient, and more connected. From intuitive voice commands to thought-controlled devices, HMIs are shaping a future where humans and machines work seamlessly together.
The possibilities are endless—are you ready to interact with the future?
Topics: Brain-Computer Interfaces Future of Interaction Gesture Control Haptic Feedback Systems HMI Technology Human-Machine Interface