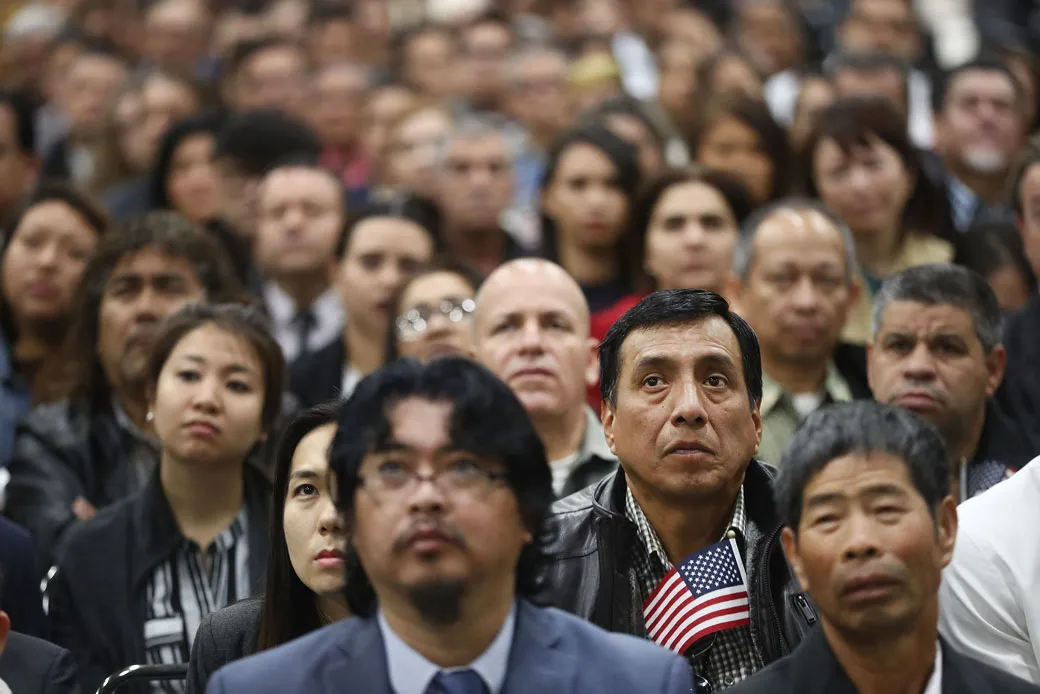
Immigration policies shape the movement of people across borders, balancing the need for national security with the ethical responsibility to protect human rights. These policies often reflect a nation’s economic priorities, cultural identity, and political landscape. Here’s a closer look at how countries around the world are managing immigration and the challenges they face.
Global Trends in Immigration Policies
Countries vary widely in their approach to immigration, but common trends include:
- Increased Border Security: Nations are investing in technology, personnel, and physical barriers to control entry.
- Focus on Skilled Migration: Many countries prioritize immigrants with skills that align with labor market needs.
- Stricter Asylum Procedures: Refugee applications are increasingly scrutinized, leading to longer processing times.
- Temporary Work Programs: Seasonal and contract-based migration policies cater to economic demands without granting permanent residency.
The United States: Balancing Opportunity and Control
The U.S. has long been a destination for immigrants seeking better opportunities. Current policies reflect:
- Tightened Border Controls: Increased surveillance and physical barriers along the U.S.-Mexico border.
- Skilled Worker Preferences: Programs like H-1B visas prioritize high-skilled labor.
- Asylum Challenges: A growing backlog of asylum cases and stricter criteria for approval.
The European Union: Managing Freedom of Movement and Crises
The EU faces unique challenges with its open-border Schengen Agreement and influx of migrants from conflict zones. Key aspects include:
- Freedom of Movement: EU citizens can live and work across member states, fostering economic integration.
- Migration Crisis Management: Southern states like Greece and Italy often bear the brunt of arrivals, leading to calls for equitable distribution among member countries.
Canada and Australia: Immigration as a Growth Strategy
Both countries use immigration to address labor shortages and demographic challenges:
- Point-Based Systems: Immigrants are assessed based on skills, education, and work experience.
- Humanitarian Focus: Canada has robust refugee resettlement programs, while Australia’s policies face criticism for offshore detention centers.
Refugee Policies and Humanitarian Concerns
Immigration policies are tested during humanitarian crises:
- Syrian Civil War: Countries like Turkey, Lebanon, and Jordan host millions of refugees, while Western nations debate resettlement quotas.
- Afghan Refugees: The Taliban’s resurgence has led to a new wave of displacement, challenging global refugee systems.
Challenges in Balancing Security and Humanity
Striking a balance between security and humanitarian obligations is difficult:
- National Security Concerns: Governments fear unchecked migration could allow the entry of criminals or terrorists.
- Economic Strain: Host countries face financial and infrastructural challenges in integrating large numbers of migrants.
- Rising Xenophobia: Anti-immigration sentiment often complicates policy-making.
Innovative Approaches to Immigration
Some nations are finding creative ways to address immigration challenges:
- Germany’s Integration Programs: Language courses and job training for migrants to ease integration.
- Digital Nomad Visas: Countries like Estonia and Barbados attract remote workers with flexible visa options.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration with NGOs and businesses to support migrant integration.
The Role of International Organizations
Global organizations play a key role in managing immigration:
- UNHCR: Advocates for refugees and coordinates resettlement efforts.
- IOM (International Organization for Migration): Provides technical and operational support for migration management.
- Global Compacts on Migration: Frameworks for international cooperation on safe and orderly migration.
Moving Toward Equitable Policies
To balance security and humanity, governments must focus on:
- Streamlining Processes: Reducing bureaucracy for asylum seekers and skilled workers.
- Investing in Integration: Providing education, housing, and employment opportunities for migrants.
- International Collaboration: Sharing responsibility for global migration challenges.
Topics: Asylum Seekers Border Control Global Migration Humanitarian Aid Immigration Policies International Cooperation Migration Challenges National Security Refugee Crisis Skilled Immigration