Vietnam, with its long coastline and diverse ecosystems, is one of the countries most vulnerable to climate change. Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and shifting agricultural patterns are already impacting millions of lives and livelihoods. However, the country is not just grappling with these challenges; communities and policymakers are taking proactive steps to mitigate the effects of climate change and adapt to a changing environment.
The Challenges of Climate Change in Vietnam
- Rising Sea Levels
- Vietnam’s extensive coastline and low-lying Mekong Delta make it highly susceptible to rising sea levels.
- Impact: Saltwater intrusion threatens freshwater supplies and agricultural productivity, particularly rice farming.
- Example: The Mekong Delta, which produces 50% of Vietnam’s rice, is experiencing severe flooding and salinization.
- Extreme Weather Events
- Vietnam is increasingly affected by typhoons, heavy rainfall, and heatwaves.
- Impact: Damage to infrastructure, homes, and crops; increased risk of landslides in mountainous regions.
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Climate change disrupts ecosystems, endangering plant and animal species, especially in coastal and forested areas.
- Example: Coral reefs and mangroves are deteriorating, affecting marine life and fisheries.
- Urban Challenges
- Rapid urbanization compounds climate risks, with cities like Ho Chi Minh City facing flooding and heat stress.
- Agricultural Shifts
- Changing rainfall patterns and rising temperatures are impacting traditional farming cycles.
- Impact: Decline in crop yields and increased pest infestations.
Community Solutions and Adaptation Efforts
- Mangrove Restoration
- Coastal communities are planting mangroves to combat erosion, buffer against storms, and support marine biodiversity.
- Example: Projects in the Red River Delta and Mekong Delta have successfully restored thousands of hectares of mangroves.
- Sustainable Agriculture
- Farmers are adopting climate-resilient practices, such as:
- Using salt-tolerant rice varieties.
- Diversifying crops to reduce dependency on rice farming.
- Implementing water-saving irrigation systems.
- Farmers are adopting climate-resilient practices, such as:
- Community-Based Disaster Preparedness
- Local programs train communities to prepare for and respond to extreme weather events.
- Example: Villages establish early warning systems and evacuation plans to reduce typhoon-related casualties.
- Urban Green Spaces
- Cities are creating parks, green roofs, and urban forests to reduce heat and absorb floodwaters.
- Example: Ho Chi Minh City is expanding its green infrastructure to combat urban flooding.
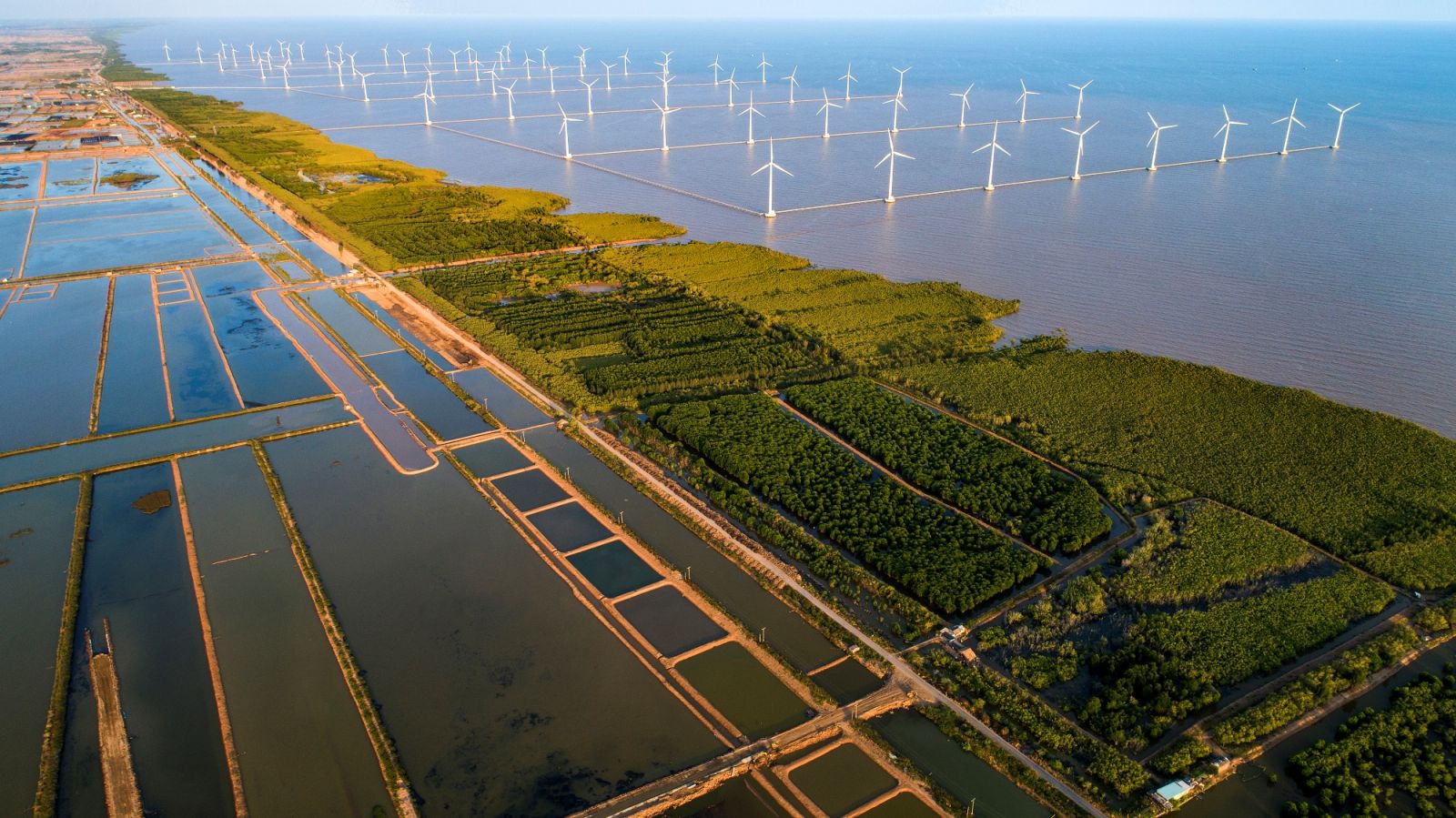
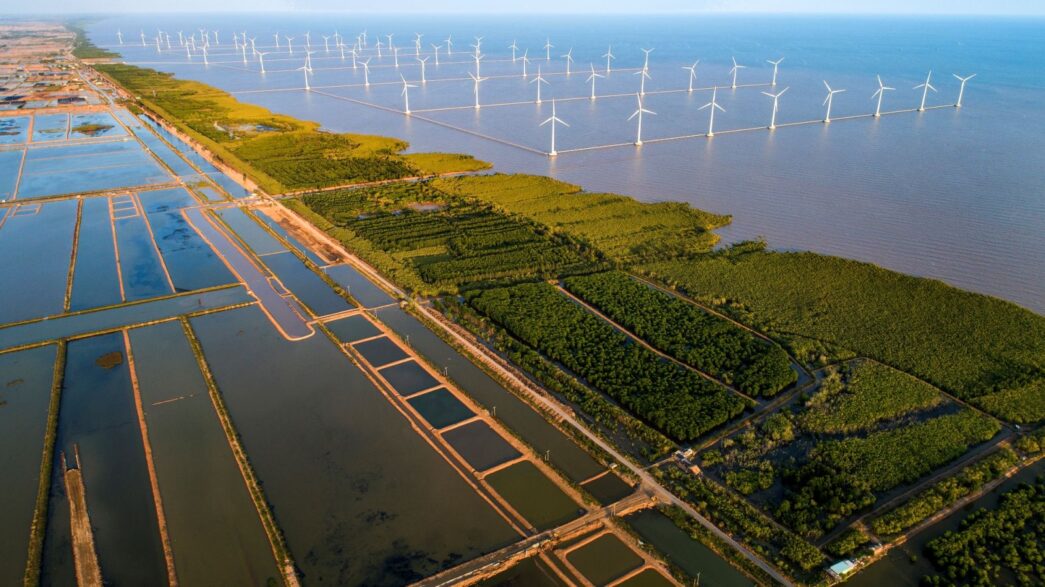
- Renewable Energy Adoption
- Solar and wind power projects are being promoted to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Example: The Trung Nam Solar Power Project in Ninh Thuan province is one of Southeast Asia’s largest solar farms.
Government Policies and International Collaboration
- National Climate Change Strategy
- Vietnam’s government has set ambitious goals, including:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Expanding renewable energy to meet 30% of the country’s energy needs by 2030.
- Protecting forests and reforesting degraded land.
- Vietnam’s government has set ambitious goals, including:
- Paris Agreement Commitments
- Vietnam is a signatory to the Paris Agreement and has pledged to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
- International Support
- Collaborations with organizations like the World Bank and United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) have provided funding and technical expertise for climate adaptation projects.
The Role of Individuals in Combating Climate Change
- Adopting Eco-Friendly Practices
- Reducing waste, conserving energy, and using sustainable products.
- Participating in Community Initiatives
- Joining mangrove restoration projects, waste cleanup drives, or local awareness campaigns.
- Promoting Climate Education
- Advocating for climate change education in schools and public forums to build awareness.
Future Prospects for Vietnam
- Innovative Technology
- Investments in green technology and climate-resilient infrastructure will shape Vietnam’s sustainable future.
- Youth Involvement
- Vietnam’s young population is increasingly active in environmental advocacy, creating momentum for long-term change.
- Global Leadership
- As Vietnam continues to innovate and adapt, it has the potential to become a leader in climate resilience within Southeast Asia.
Climate change presents significant challenges to Vietnam, but the country’s resilience and proactive approach offer hope for a sustainable future. Through government policies, community efforts, and international collaboration, Vietnam is taking bold steps to address these issues. By continuing to focus on innovation, education, and sustainability, Vietnam can lead the way in combating climate change and protecting its people and ecosystems.
Topics: Climate Change Vietnam Disaster Preparedness Environmental Solutions Vietnam Flood Management Mangrove Restoration Mekong Delta Paris Agreement Renewable Energy Sustainable Agriculture Urban Green Spaces