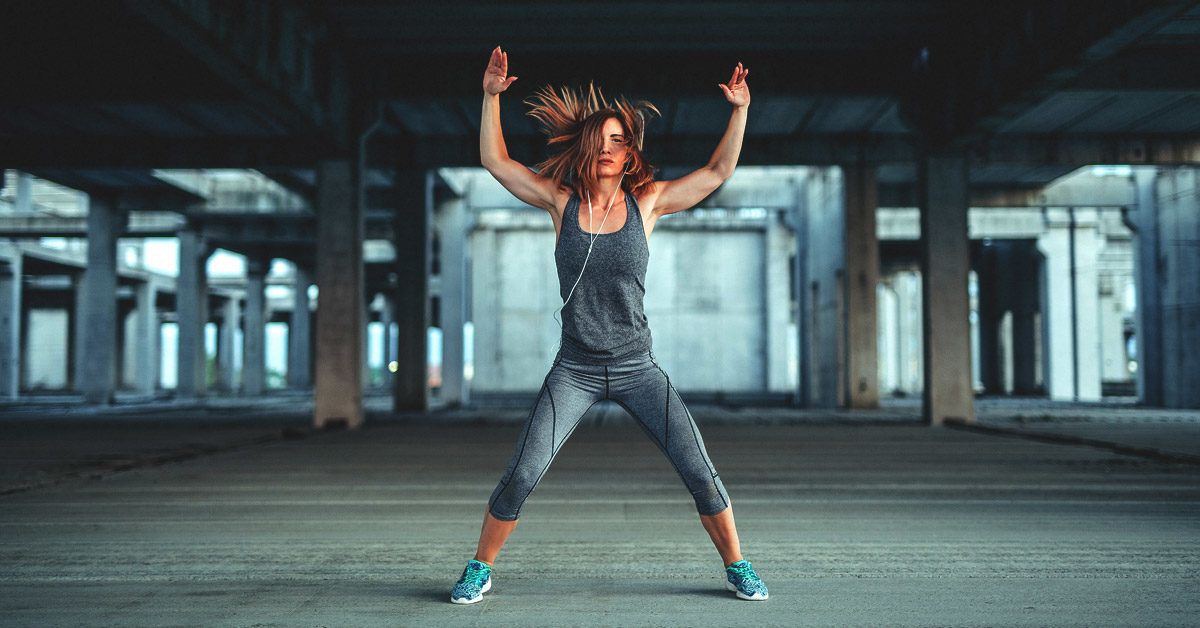
Cardiovascular endurance, often called aerobic fitness, refers to the ability of your heart, lungs, and blood vessels to supply oxygen-rich blood to your muscles during sustained physical activity. It’s a key component of overall fitness, essential for maintaining energy, stamina, and long-term health. Whether you’re running, swimming, or cycling, improving your cardiovascular endurance can enhance your physical performance and boost your quality of life.
What is Cardiovascular Endurance?
Cardiovascular endurance is the efficiency with which your cardiovascular system (heart, lungs, and blood vessels) delivers oxygen to your body during prolonged exercise. It also measures how well your muscles use that oxygen to produce energy.
Benefits of Cardiovascular Endurance
- Heart Health:
- Strengthens the heart muscle, improving its ability to pump blood efficiently.
- Reduces the risk of heart disease, hypertension, and stroke.
- Increased Energy Levels:
- Improves stamina, allowing you to perform daily tasks and physical activities with less fatigue.
- Weight Management:
- Burns calories, helping you maintain or lose weight.
- Better Lung Function:
- Enhances oxygen uptake and respiratory efficiency.
- Improved Mental Health:
- Releases endorphins that reduce stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance:
- Increases the ability to sustain high-intensity activities for longer periods.
- Longevity:
- Associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases and increased life expectancy.
Examples of Cardiovascular Endurance Exercises
- Running or Jogging:
- Excellent for building endurance and burning calories.
- Options: Treadmill running, road running, trail running.
- Cycling:
- Improves leg strength and cardiovascular fitness.
- Options: Outdoor cycling or stationary biking.
- Swimming:
- A full-body workout that enhances endurance while being gentle on the joints.
- Walking:
- A low-impact option for beginners to improve heart health and stamina.
- Rowing:
- Combines cardiovascular and strength training in one activity.
- Dancing:
- Fun and engaging way to boost endurance and coordination.
- Jump Rope:
- A high-intensity workout that increases heart rate and endurance quickly.
- HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training):
- Alternates between short bursts of intense activity and rest, effectively improving endurance in less time.
How to Measure Cardiovascular Endurance
- VO2 Max:
- The maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during exercise. Higher VO2 max indicates better endurance.
- Measured using fitness tests or devices.
- Heart Rate:
- Monitor your resting heart rate and recovery rate after exercise. A lower resting heart rate and quicker recovery indicate better endurance.
- Distance or Time Tests:
- Track how far or how long you can sustain an activity like running or cycling.
- Step Test:
- Use a standardized step test to measure your heart rate response and endurance levels.
How to Improve Cardiovascular Endurance
- Gradual Progression:
- Start with moderate-intensity activities and gradually increase intensity, duration, or frequency.
- Mix It Up:
- Incorporate different types of cardio exercises to keep workouts engaging and target various muscle groups.
- Follow the FITT Principle:
- Frequency: Exercise 3–5 times per week.
- Intensity: Aim for 60–80% of your maximum heart rate.
- Time: Start with 20–30 minutes per session and increase gradually.
- Type: Choose aerobic activities like running, swimming, or cycling.
- Interval Training:
- Alternate between high-intensity and low-intensity exercises to boost stamina efficiently.
- Active Recovery:
- Include low-intensity workouts like walking or yoga on rest days to maintain endurance without overexertion.
- Monitor Your Progress:
- Use fitness trackers or apps to track your heart rate, distance, and time.
Safety Tips for Cardiovascular Training
- Warm-Up and Cool Down:
- Prepare your body with dynamic stretches and light cardio before starting.
- Cool down with static stretches to prevent stiffness.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink water before, during, and after your workout.
- Listen to Your Body:
- Avoid overtraining and take rest days to allow recovery.
- Wear Proper Gear:
- Use appropriate footwear and clothing for your activity.
- Consult a Professional:
- Seek guidance if you’re new to exercise or have pre-existing health conditions.
Cardiovascular Endurance and Other Fitness Components
- Strength Training:
- Improves muscular endurance and complements cardio workouts.
- Flexibility:
- Enhances range of motion and reduces the risk of injury during cardio activities.
- Balance and Core Stability:
- Supports posture and efficiency in aerobic exercises.
Cardiovascular endurance is a cornerstone of fitness, essential for a healthy and active lifestyle. Whether your goal is to run a marathon, improve energy levels, or reduce the risk of chronic disease, building endurance through consistent aerobic exercise offers lifelong benefits. By incorporating diverse cardio activities, staying motivated, and tracking progress, you can achieve a stronger heart, fitter body, and healthier mind.
Are you ready to elevate your fitness and boost your cardiovascular health?
Topics: Aerobic Fitness Cardio Workouts Cardiovascular Endurance Fitness Tips Healthy Living Heart Health Stamina